Data Visualization with Virtual Reality Explored

Introduction: Unlocking the Power of Data Visualization in VR
In the ever-evolving landscape of data analysis and presentation, the emergence of virtual reality (VR) has opened up new frontiers for data visualization. As the digital world continues to converge with the physical, the ability to immerse users in data-driven environments has become a game-changer, revolutionizing the way we perceive, interact, and derive insights from complex information.
The integration of data visualization and virtual reality has the potential to transform how we engage with data, offering unprecedented levels of interactivity, depth, and spatial understanding. By leveraging the inherent advantages of VR, such as its three-dimensional (3D) capabilities, intuitive user interfaces, and sense of presence, data visualization in virtual environments can unlock new possibilities for data exploration, decision-making, and knowledge sharing.

In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of data visualization with virtual reality, exploring the latest advancements, practical applications, and the various ways in which this powerful combination can enhance our understanding and analysis of data.
The Rise of Data Visualization in Virtual Reality
Understanding the Advantages of VR for Data Visualization
The immersive nature of virtual reality offers several advantages that make it a compelling platform for data visualization:
Spatial Awareness and Depth Perception: The 3D environment of VR allows users to perceive data in a more natural and intuitive way, providing a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and patterns within the data.
Interactivity and Manipulation: VR enables users to interact with data in real-time, allowing them to manipulate, filter, and explore visualizations through intuitive gestures and controls, fostering a more engaging and hands-on experience.
Scalability and Flexibility: VR can accommodate the display of large, complex datasets, enabling users to navigate and analyze information at different scales, from high-level overviews to granular details.
Collaborative Experiences: VR can facilitate remote or co-located collaboration, enabling multiple users to explore and discuss data visualizations simultaneously, promoting knowledge sharing and collective decision-making.
Immersive Storytelling: The immersive nature of VR can be leveraged to create engaging narratives and data-driven experiences, allowing users to become fully immersed in the data and its underlying insights.

Emerging Trends and Technologies in VR-based Data Visualization
As the field of data visualization in virtual reality continues to evolve, several emerging trends and technologies are shaping the future of this dynamic landscape:
Volumetric Data Visualization: The ability to visualize and interact with 3D volumetric data, such as medical scans, geological data, or scientific simulations, is becoming increasingly prevalent in VR-based data visualization.
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: The blending of virtual and physical environments through AR is enabling new ways of integrating data visualizations into real-world contexts, enhancing the accessibility and relevance of data insights.
Multimodal Interaction: Advancements in VR input devices, including hand tracking, eye-tracking, and voice control, are enabling more intuitive and natural ways of interacting with data visualizations, further enhancing the user experience.
Data Annotation and Collaboration: VR-based data visualization platforms are incorporating features that allow users to annotate, comment, and collaborate on data insights, fostering a shared understanding and facilitating decision-making processes.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): The integration of AI and ML algorithms is enabling intelligent data analysis, automated insights, and personalized visualization recommendations within VR-based data exploration environments.

Overcoming Challenges and Limitations
While the benefits of data visualization in virtual reality are substantial, there are also challenges and limitations that need to be addressed:
Hardware Accessibility: The widespread adoption of VR-based data visualization can be hindered by the cost and accessibility of high-quality VR hardware, limiting its reach and implementation in certain industries or applications.
Motion Sickness and User Comfort: Some users may experience motion sickness or discomfort when immersed in VR environments, particularly during extended periods of use, which can impact the overall user experience and adoption.
Data Integration and Compatibility: Integrating various data sources and formats into a cohesive VR-based visualization can be technically complex, requiring specialized expertise and software solutions.
Scalability and Performance: Rendering large, complex datasets in a VR environment can pose challenges in terms of system performance, data processing, and visual optimization, especially on lower-end hardware.
User Training and Adoption: Transitioning from traditional 2D data visualization to immersive VR-based experiences may require additional user training and familiarization, which can slow down the adoption process in some organizations.

Practical Applications of Data Visualization in Virtual Reality
Exploring Data in 3D Environments
One of the primary advantages of data visualization in virtual reality is the ability to explore data in a fully immersive 3D environment. This approach allows users to perceive and interact with data in a more intuitive and natural way, revealing insights that may be challenging to discern in traditional 2D visualizations.
VR-based data visualization can be particularly beneficial in fields such as:
-
Scientific Visualization: Researchers can use VR to visualize and explore complex scientific data, such as molecular structures, astronomical simulations, or fluid dynamics, gaining a deeper understanding of the underlying phenomena.
-
Geospatial Analysis: VR enables the visualization and exploration of geospatial data, allowing users to navigate through 3D terrain, analyze spatial patterns, and make more informed decisions related to urban planning, resource management, or transportation.
-
Medical Imaging: Healthcare professionals can leverage VR to visualize and interpret medical scans, such as MRI or CT scans, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of anatomical structures and facilitating diagnostic procedures and surgical planning.
-
Financial Data Analysis: Financial analysts and investment professionals can use VR-based data visualization to explore complex financial data, identify patterns, and make more informed investment decisions by experiencing the data in an immersive 3D environment.
Enhancing Data Storytelling and Presentation
Virtual reality offers a unique opportunity to elevate data storytelling and presentation, transforming static visualizations into dynamic, immersive experiences. By leveraging the spatial capabilities of VR, data visualization can be integrated into captivating narratives, allowing users to become actively engaged with the data and its underlying insights.

Some key applications of VR-based data storytelling and presentation include:
-
Data-Driven Journalism: Journalists can use VR to create engaging, data-driven stories that immerse readers in the data, enhancing their understanding and emotional connection to the subject matter.
-
Corporate Reporting and Presentations: Companies can leverage VR to present financial reports, market trends, or business strategies in a more impactful and memorable way, fostering deeper engagement with stakeholders and decision-makers.
-
Educational and Training Experiences: VR-based data visualization can be integrated into educational and training contexts, enabling students or trainees to explore data-driven simulations, visualizations, and interactive scenarios, enhancing their learning and retention.
-
Data Visualization Exhibitions: Museums, science centers, and other cultural institutions can create immersive data visualization exhibits that allow visitors to explore and interact with complex data in a captivating and educational manner.
Collaborative Data Exploration and Decision-Making
One of the unique advantages of data visualization in virtual reality is the ability to facilitate collaborative experiences, enabling multiple users to explore and discuss data insights simultaneously, even across remote locations.

Some key applications of collaborative VR-based data visualization include:
-
Remote Team Collaboration: VR can enable distributed teams to come together in a shared virtual environment, allowing them to jointly analyze data, brainstorm solutions, and make informed decisions, regardless of their physical locations.
-
Data-Driven Workshops and Ideation Sessions: VR-based data visualization can be used to facilitate interactive workshops and ideation sessions, where participants can collectively explore, manipulate, and derive insights from data, fostering a more engaged and productive collaboration.
-
Virtual Meetings and Presentations: VR can transform traditional virtual meetings and presentations into more engaging and interactive experiences, where participants can not only view data visualizations but also actively participate in discussions and decision-making processes.
-
Virtual Classrooms and Learning Environments: VR-based data visualization can be incorporated into virtual classrooms and learning environments, enabling students to collaborate on data-driven projects, share insights, and engage in interactive learning activities.
Integrating VR with Augmented Reality (AR)
The convergence of virtual reality and augmented reality (AR) is opening up new possibilities for data visualization, blending the virtual and physical worlds to create innovative, context-aware solutions.
Some key applications of integrating VR and AR for data visualization include:
-
Visualizing Data in Physical Spaces: AR can enable the overlay of data visualizations directly onto the real-world environment, allowing users to interpret and interact with data in the context of their physical surroundings, such as a factory floor, a city landscape, or a medical facility.
-
Combining Virtual and Physical Interactions: By integrating VR and AR, users can seamlessly transition between immersive virtual environments and physical interactions, allowing them to manipulate data visualizations using both virtual and tangible controls, enhancing the overall user experience.
-
Bridging the Gap between Digital and Physical: The combination of VR and AR can help bridge the gap between digital data and physical reality, enabling users to better understand the relationships and implications of data within the real world, supporting decision-making and problem-solving.
-
Enhancing Spatial Awareness and Navigation: The integration of VR and AR can provide users with a more comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships, allowing them to navigate complex data visualizations while maintaining a strong sense of their physical surroundings.
Exploring Emerging Applications and Use Cases
As the field of data visualization in virtual reality continues to evolve, new and innovative applications are emerging across a wide range of industries and domains. Some emerging use cases include:
Urban Planning and Smart City Development: VR-based data visualization can be used to model and simulate urban environments, enabling city planners, architects, and policymakers to analyze data related to traffic patterns, infrastructure, land use, and environmental factors, facilitating more informed decision-making.
Manufacturing and Industrial Optimization: VR can be leveraged to visualize and analyze data from manufacturing processes, production lines, and supply chain operations, allowing engineers and operations managers to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and simulate potential improvements.
Disaster Management and Emergency Response: VR-based data visualization can be employed in emergency management scenarios, enabling first responders and disaster relief teams to visualize and analyze real-time data related to natural disasters, infrastructure damage, and resource allocation, improving emergency planning and response coordination.
Retail and Customer Experience: Retailers can use VR-based data visualization to gain insights into customer behavior, store layout, and product placement, optimizing the in-store experience and supporting data-driven merchandising decisions.
Sports Performance Analysis: Athletes, coaches, and sports analysts can leverage VR to visualize and analyze performance data, such as player movements, team tactics, and game statistics, enabling more informed strategy development and player training.

As the integration of data visualization and virtual reality continues to evolve, the potential applications and use cases will only continue to expand, unlocking new opportunities for data-driven decision-making, problem-solving, and knowledge sharing across various industries and domains.
Best Practices and Considerations for Effective VR-based Data Visualization
Leveraging the power of data visualization in virtual reality requires a thoughtful approach to ensure the effective and meaningful presentation of information. Here are some best practices and considerations to keep in mind:
User-Centric Design
Prioritize the user experience by designing VR-based data visualizations that are intuitive, accessible, and tailored to the specific needs and goals of the target audience. Consider factors such as user familiarity, cognitive load, and physical comfort to create visualizations that enhance, rather than hinder, the users' understanding and engagement.
Visual Optimization and Performance
Ensure that the VR-based data visualizations are optimized for performance, ensuring smooth rendering and responsive interactions, even with complex datasets. Utilize techniques such as data aggregation, level-of-detail rendering, and hardware acceleration to maintain high-quality visuals and seamless user experiences.
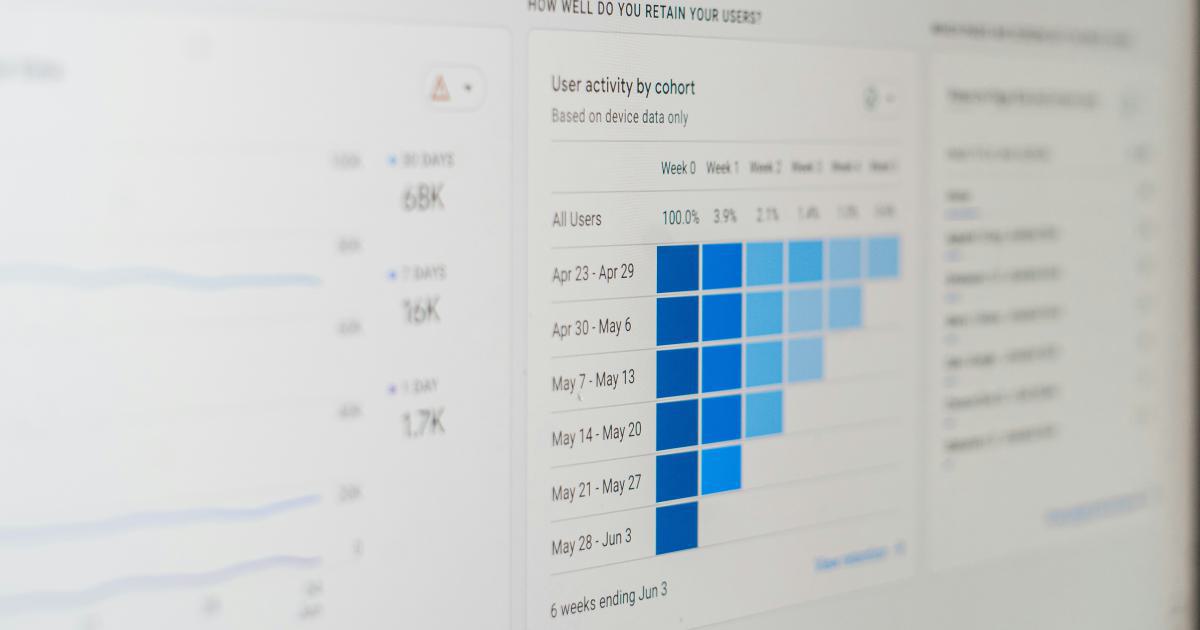
Intuitive Interaction and Navigation
Develop intuitive and natural interaction methods that allow users to easily navigate, manipulate, and explore the data visualizations within the VR environment. Leverage VR input devices, such as hand controllers or eye-tracking, to enable seamless interactions that feel integrated with the virtual experience.
Data Dimensionality and Representation
Carefully consider the dimensionality of the data and how it can be effectively represented within the 3D VR environment. Utilize techniques such as data aggregation, spatial mapping, and multi-dimensional visualization to ensure that the data is presented in a clear and comprehensible manner.
Collaborative Workflows and Annotation
Incorporate features that enable collaborative data exploration and decision-making, such as shared virtual workspaces, real-time annotations, and integrated communication tools. This can foster a sense of collective understanding and facilitate more effective knowledge sharing and problem-solving.

Iterative Refinement and User Feedback
Continuously gather user feedback and engage in iterative refinement of the VR-based data visualizations. Regularly evaluate the effectiveness, usability, and overall impact of the visualizations, and make necessary adjustments to ensure they remain relevant, impactful, and aligned with the evolving needs of the users.

By adhering to these best practices and considerations, you can create VR-based data visualizations that effectively harness the power of virtual reality, delivering engaging, informative, and impactful experiences for your users.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Data Visualization with Virtual Reality
As we've explored in this comprehensive article, the integration of data visualization and virtual reality has the potential to revolutionize the way we perceive, interact, and derive insights from complex information. By leveraging the inherent advantages of VR, such as its 3D capabilities, intuitive user interfaces, and sense of presence, data visualization in virtual environments can unlock new possibilities for data exploration, decision-making, and knowledge sharing.
From enhancing data storytelling and presentation to enabling collaborative data exploration and integrating VR with augmented reality, the applications of this dynamic intersection are vast and constantly evolving. As the field continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and impactful use cases emerge, transforming the way we understand and interact with data.
However, the successful implementation of data visualization in virtual reality requires a thoughtful approach, considering user-centric design, visual optimization, intuitive interaction, and collaborative workflows. By embracing these best practices and continuously refining the user experience, organizations can harness the full potential of this powerful combination to drive data-driven decision-making, foster innovation, and unlock new levels of understanding and insight.
As we look to the future, the integration of data visualization and virtual reality promises to be a transformative force, paving the way for a more immersive, engaging, and impactful data-driven world. By embracing this convergence, we can unlock the true power of information, empowering individuals, organizations, and communities to navigate the complexities of the digital age with greater clarity, agility, and success.