Decoding Visual Perception for Impactful Data Communication


Our world is increasingly driven by data, and the ability to effectively communicate that data is becoming increasingly crucial. In this comprehensive article, we'll explore the fundamental principles of visual perception and uncover how they can be leveraged to create impactful data visualizations that captivate audiences and drive meaningful insights.
The Power of Visual Perception
At the heart of effective data communication lies an understanding of how the human visual system processes information. Our eyes and brain work together seamlessly to transform light, color, and form into the rich tapestry of our perceived reality. By tapping into the innate capabilities of our visual system, we can design data visualizations that resonate on a deep, intuitive level.
The Human Visual System
The human eye is a remarkable feat of evolution, capable of detecting a vast range of light wavelengths and translating them into electrical signals that the brain can interpret. The retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye, contains two primary types of photoreceptor cells: rods and cones.

Rods are responsible for detecting brightness and movement, while cones are specialized for color vision. The distribution and concentration of these cells across the retina play a crucial role in our visual perception, influencing how we perceive and process information.
Gestalt Principles
Beyond the physical structure of the eye, the way our brain processes visual information is equally essential to effective data communication. The Gestalt principles, a set of laws governing how we perceive and organize visual elements, provide a powerful framework for designing intuitive and engaging data visualizations.

These principles, such as proximity, similarity, continuity, and closure, describe how our brain tends to group and interpret visual elements. By aligning our data visualizations with these innate perceptual tendencies, we can create representations that are instantly comprehensible and memorable.
Harnessing Visual Perception for Data Visualization
Now that we have a foundational understanding of the human visual system and the Gestalt principles, let's explore how to apply these insights to the design of effective data visualizations.
Color and Contrast
Color is a fundamental building block of visual perception, and it plays a crucial role in data visualization. The strategic use of color can enhance the clarity, legibility, and emotional impact of your visualizations.

Leveraging color theory, you can create palettes that highlight key insights, differentiate data categories, and evoke specific emotional responses. Appropriate use of contrast, both in color and brightness, can guide the viewer's attention and ensure important information is immediately accessible.
Visual Hierarchy and Emphasis
Just as the Gestalt principles govern how we group and perceive visual elements, the concept of visual hierarchy dictates how we prioritize and focus on information within a data visualization.

By strategically using size, position, and other visual cues, you can establish a clear hierarchy that guides the viewer's eye to the most critical data points and insights. Emphasis techniques, such as the use of annotations, callouts, and layering, can further highlight the most important information and draw the viewer's attention where it matters most.
Simplicity and Clarity
In the realm of data communication, less is often more. Overloading visualizations with excessive information or complex design elements can quickly lead to cognitive overload and confusion.

The principles of simplicity and clarity are essential for creating visualizations that are easily understood and readily interpretable. By prioritizing the most relevant data, using clear and unambiguous visual representations, and minimizing clutter, you can ensure your visualizations convey their message with maximum impact.
Storytelling and Engagement
Data visualization is not just about presenting facts and figures; it's about crafting a compelling narrative that engages the viewer and inspires action. By incorporating storytelling techniques, you can transform your data into a captivating journey that resonates on an emotional level.
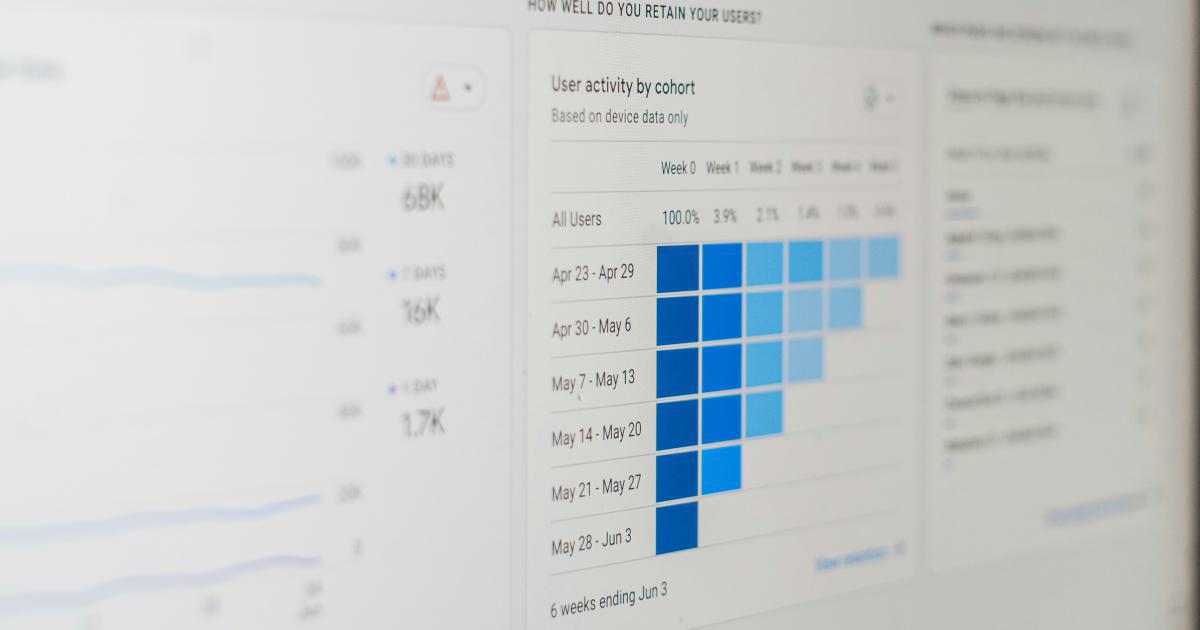
Through the strategic use of visual metaphors, narratives, and interactive elements, you can guide the viewer through your data, highlighting key insights and guiding them towards a deeper understanding. This approach not only makes your visualizations more engaging but also increases the likelihood of your message leaving a lasting impression.
Designing Impactful Data Visualizations
With a solid understanding of visual perception and the principles of effective data visualization, let's delve into the practical steps of designing impactful data visualizations.
Understand Your Audience
The first and most crucial step in creating effective data visualizations is to deeply understand your target audience. Who are they, what are their goals and pain points, and how do they prefer to consume information? By tailoring your visualizations to the specific needs and preferences of your audience, you can ensure your message resonates and drives the desired action.
Define Your Objectives
Before diving into the design process, it's essential to clearly define the objectives of your data visualization. What are you trying to achieve – inform, persuade, or inspire? Aligning your design decisions with these specific goals will help you create visualizations that are laser-focused and impactful.
Choose the Right Visualization Type
With your audience and objectives in mind, you can now select the most appropriate data visualization type. From bar charts and scatter plots to treemaps and network diagrams, each visualization style has its own strengths and weaknesses. Choose the one that best aligns with the nature of your data and the insights you want to convey.
Optimize for Clarity and Legibility
As you design your data visualizations, keep the principles of visual perception and Gestalt theory at the forefront of your mind. Ensure that your visualizations are clear, unambiguous, and easy to interpret. Use color, contrast, and visual hierarchy to guide the viewer's attention and highlight the most critical information.
Incorporate Storytelling Elements
To truly captivate your audience and drive meaningful insights, weave a compelling narrative into your data visualizations. Use visual metaphors, annotations, and interactive features to guide the viewer through the data and reveal the underlying stories. This approach not only enhances engagement but also makes your visualizations more memorable and impactful.
Iteratively Test and Refine
Creating effective data visualizations is an iterative process. Continuously gather feedback, test your designs with representative users, and refine your approach based on their insights. This feedback loop will help you identify and address any pain points or areas for improvement, ensuring your final visualizations are as impactful as possible.

Bringing It All Together: Case Studies
To illustrate the practical application of the principles we've discussed, let's explore a few real-world examples of impactful data visualizations.
Example 1: Visualizing Global Poverty
In this example, the Gapminder Foundation uses a scatter plot visualization to illustrate the relationship between income, life expectancy, and population size across different countries.

By leveraging the Gestalt principle of continuity, the visualization effectively guides the viewer's eye through the data points, highlighting key trends and insights. The use of color, size, and animation further enhances the clarity and storytelling elements of the visualization, making complex global data accessible and engaging.
Example 2: Tracking the Spread of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has sparked an influx of data visualizations aimed at tracking the spread of the virus. One notable example is the visualization created by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University.
This visualization utilizes a clear and intuitive map-based design, leveraging color and size to convey the severity of the outbreak in different regions. The incorporation of time-series data and interactive features allows users to explore the dynamic nature of the pandemic, fostering a deeper understanding of the unfolding situation.
Example 3: Visualizing Gender Inequality
The "Equality between Men and Women" visualization by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) demonstrates the power of data visualization in addressing complex social issues.

By employing a clean, minimalist design and a carefully curated color palette, this visualization effectively highlights the discrepancies between men and women across various indicators, such as employment, education, and political representation. The use of simple, yet compelling, visual metaphors helps the viewer quickly grasp the magnitude and nuances of gender inequality.
These examples illustrate how the principles of visual perception and effective data visualization can be applied to create impactful, engaging, and informative data representations that drive meaningful insights and inspire action.
Conclusion
In the data-driven world we inhabit, the ability to communicate complex information effectively has become a critical skill. By understanding the fundamental principles of visual perception and leveraging them in the design of data visualizations, we can create representations that captivate audiences, drive meaningful insights, and inspire action.
As you embark on your journey of crafting impactful data visualizations, remember to keep the needs of your audience at the forefront, define clear objectives, and prioritize simplicity and clarity. Incorporate storytelling elements and continuously iterate based on user feedback to refine your approach and maximize the impact of your data communication efforts.
The future of data-driven decision-making relies on our ability to transform raw information into visually compelling and intuitively understandable representations. By mastering the art of visual perception and applying it to data visualization, you can unlock the full potential of your data and drive meaningful change in your organization and beyond.