What Are Google Analytics Calculated Metrics And How To Use Them?

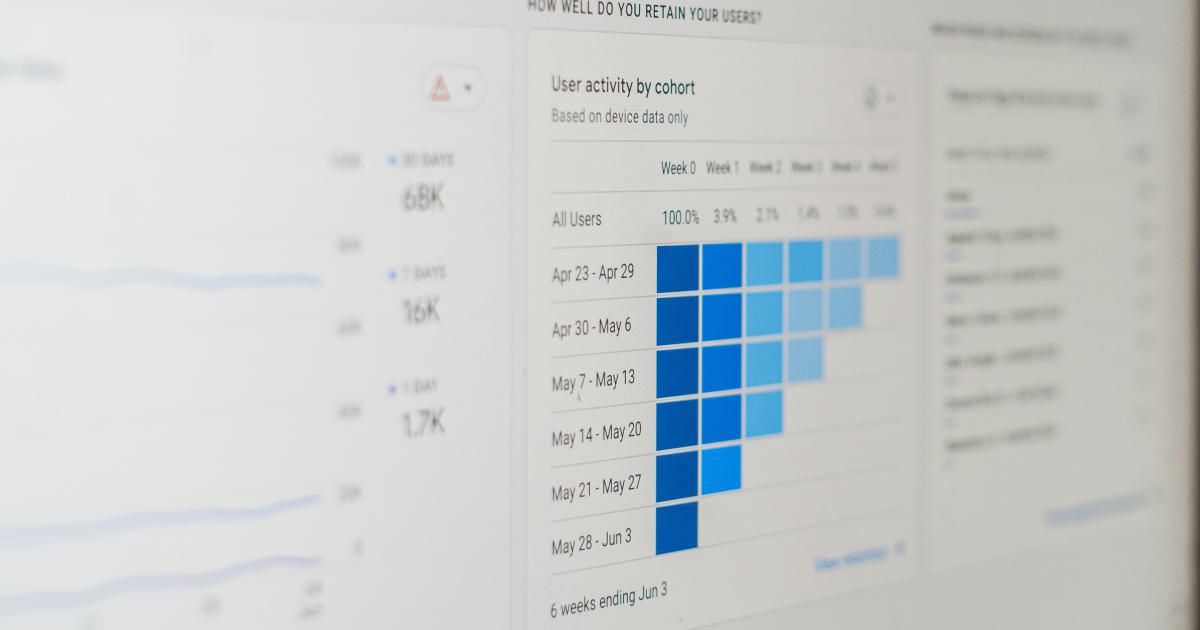
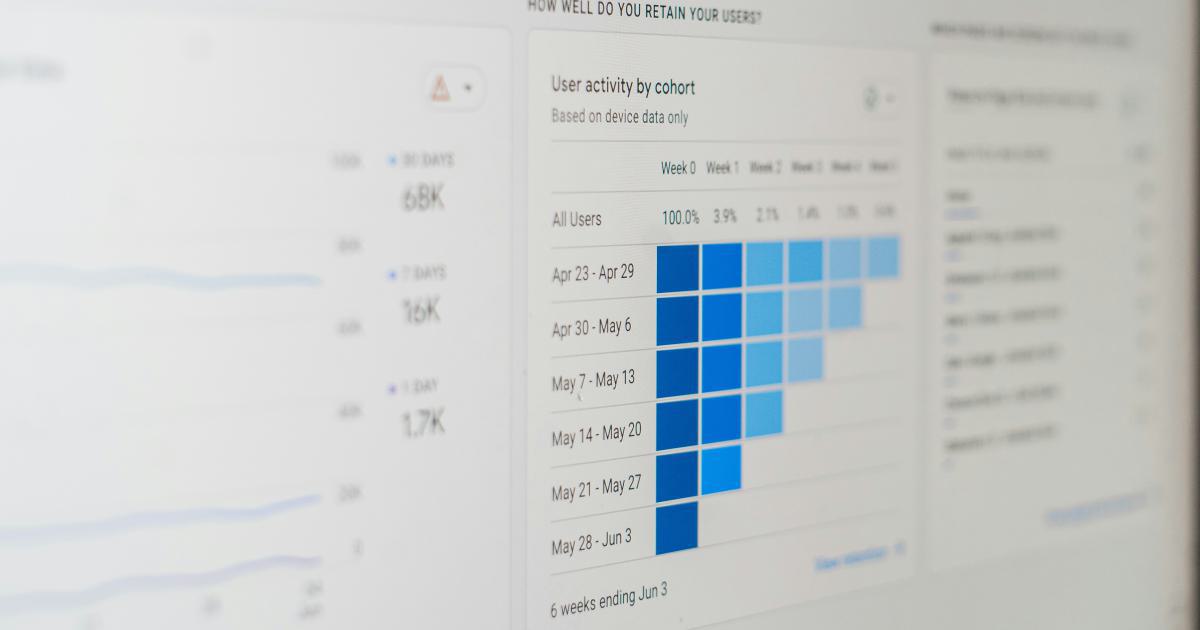
Introduction to Google Analytics Calculated Metrics
Google Analytics is a powerful tool for tracking and analyzing website performance, user behavior, and marketing effectiveness. While the platform provides a wealth of standard metrics out of the box, it also offers a set of calculated metrics that can provide deeper insights into your data.
Calculated metrics are custom metrics that you can create within Google Analytics to combine multiple standard metrics in various ways. These calculated metrics allow you to gain a more nuanced understanding of your website's performance and user interactions.

In this comprehensive article, we'll explore the world of Google Analytics calculated metrics, covering what they are, how they differ from standard metrics, and how you can leverage them to drive better decision-making for your business.
Understanding Calculated Metrics in Google Analytics
Calculated metrics in Google Analytics are user-defined metrics that are derived from one or more standard metrics. They are essentially mathematical formulas that allow you to combine, manipulate, and interpret your data in more advanced ways.
Standard metrics in Google Analytics, such as "Sessions," "Bounce Rate," and "Conversion Rate," provide valuable insights, but they don't always tell the whole story. Calculated metrics enable you to create custom metrics that are tailored to your specific business needs and goals.
Benefits of Using Calculated Metrics
Calculated metrics offer several key benefits:
Deeper Insights: By combining multiple standard metrics, calculated metrics can provide a more comprehensive understanding of your website's performance and user behavior.
Customization: Calculated metrics allow you to create custom metrics that align with your unique business objectives, moving beyond the standard metrics provided by Google Analytics.
Meaningful Comparisons: Calculated metrics can help you make more meaningful comparisons across different segments of your audience, campaigns, or time periods.
Improved Decision-Making: With the additional insights gained from calculated metrics, you can make more informed decisions about your marketing strategies, website optimization, and resource allocation.
Types of Calculated Metrics
Google Analytics offers several types of calculated metrics that you can create and use. Some common examples include:
Conversion Metrics: Metrics that measure the success of your conversion goals, such as "Conversion Rate," "Revenue per Conversion," and "Cost per Conversion."
Engagement Metrics: Metrics that provide insights into how users interact with your website, such as "Pages per Session," "Average Session Duration," and "Bounce Rate."
Efficiency Metrics: Metrics that help you evaluate the efficiency of your marketing efforts, such as "Cost per Session," "Cost per Acquisition," and "Return on Ad Spend."
Custom Audience Metrics: Metrics that allow you to analyze the behavior and performance of specific user segments, such as "New User Conversion Rate" and "Returning User Bounce Rate."
By understanding the different types of calculated metrics available, you can start to identify the ones that are most relevant to your business and begin incorporating them into your data analysis and decision-making processes.
Creating Calculated Metrics in Google Analytics
To create and use calculated metrics in Google Analytics, follow these steps:
Step 1: Access the Calculated Metrics Feature
Log in to your Google Analytics account and navigate to the "Admin" section.
In the "View" column, click on the "View Settings" option.
Scroll down to the "Custom Definitions" section and click on "Calculated Metrics."
Step 2: Create a New Calculated Metric
Click on the "New Calculated Metric" button.
Provide a name for your calculated metric that clearly describes its purpose.
In the "Formula" field, enter the mathematical expression that combines the standard metrics you want to use.
Step 3: Configure the Calculated Metric
Select the appropriate metric type (e.g., Ratio, Percentage, Currency, or Number) for your calculated metric.
Determine the decimal precision you want to display for the metric.
Optionally, you can add a description to provide more context about the metric.
Step 4: Preview and Save the Calculated Metric
Use the "Preview" feature to ensure the calculated metric is functioning as intended.
Once you're satisfied with the metric, click "Save" to make it available for use in your reports.

After creating your calculated metric, you can start using it in your reports and analyses. The metric will be available in the "Customization" section of the "Metrics" dropdown menu, allowing you to easily incorporate it into your existing reports or create new ones.
Commonly Used Calculated Metrics in Google Analytics
Now that you understand the basics of creating calculated metrics, let's explore some of the most commonly used and valuable calculated metrics in Google Analytics.
Conversion Rate Metrics
Conversion Rate: Measures the percentage of users who completed a desired action (e.g., made a purchase, submitted a form, or signed up for a newsletter).
New User Conversion Rate: Measures the conversion rate specifically for new users.
Returning User Conversion Rate: Measures the conversion rate for users who have previously visited your website.
Engagement Metrics
Pages per Session: Measures the average number of pages viewed per session.
Average Session Duration: Measures the average length of a user session on your website.
Bounce Rate: Measures the percentage of users who leave your website after viewing only one page.
Efficiency Metrics
Cost per Session: Measures the average cost per session for your paid marketing campaigns.
Cost per Acquisition: Measures the average cost per conversion or goal completion.
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
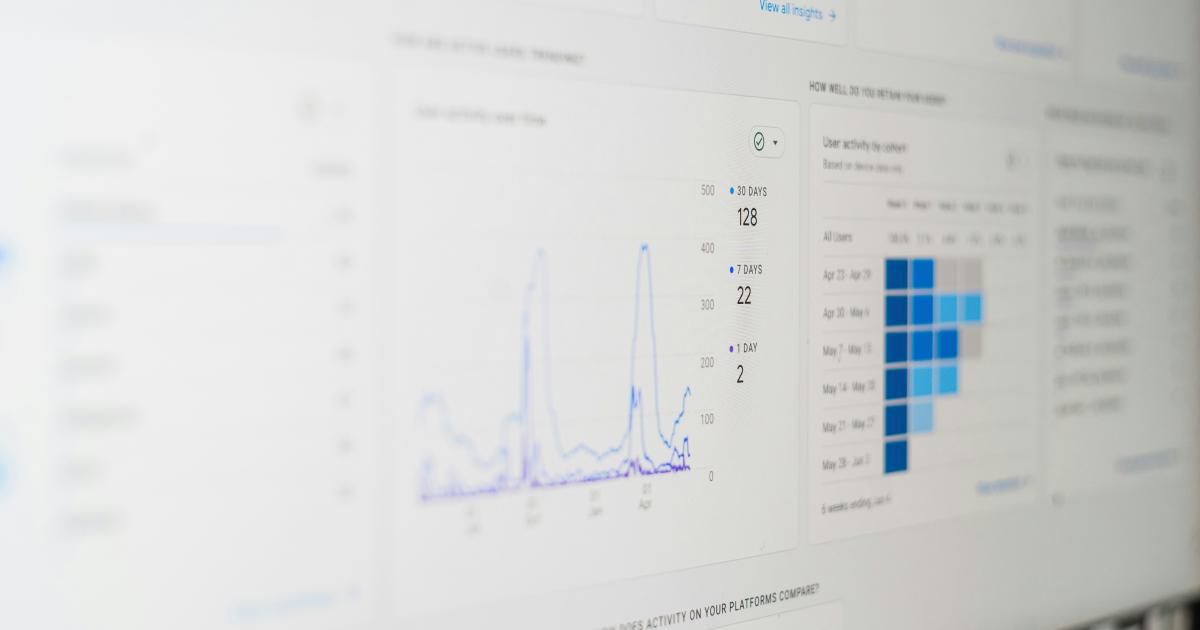
These are just a few examples of the many calculated metrics you can create in Google Analytics. The specific metrics you choose to focus on will depend on your business goals, marketing strategies, and the key performance indicators (KPIs) you're interested in tracking.
Leveraging Calculated Metrics for Better Insights
Now that you understand the basics of calculated metrics in Google Analytics, let's explore how you can leverage them to gain deeper insights and make more informed decisions.
Identifying Opportunities for Improvement
By analyzing your calculated metrics, you can uncover areas of your website or marketing efforts that need improvement. For example, if you notice a low conversion rate for a specific page or campaign, you can dig deeper to understand the underlying factors contributing to this performance.
Similarly, if you see a high bounce rate on certain pages, you can use this information to identify areas where you need to improve the user experience or content relevance.
Optimizing Marketing Campaigns
Calculated metrics can also help you optimize your marketing campaigns for better performance. By tracking metrics like "Cost per Acquisition" and "Return on Ad Spend," you can evaluate the effectiveness of your various marketing channels and adjust your budget and strategies accordingly.
For instance, if you notice that your paid social media campaigns have a higher "Cost per Acquisition" compared to your search engine marketing efforts, you may decide to reallocate more of your budget to the more efficient channel.
Segmenting and Analyzing User Behavior
Calculated metrics can also be used to segment your audience and analyze user behavior in more granular detail. For example, by creating a "New User Conversion Rate" metric, you can compare the performance of your marketing efforts in attracting and converting new users versus returning users.
This information can help you tailor your content, messaging, and user experience to the specific needs and preferences of different user segments, ultimately leading to better engagement and conversions.

Improving Decision-Making
Ultimately, the power of calculated metrics lies in their ability to inform better decision-making. By having a deeper understanding of your website's performance and user behavior, you can make more informed decisions about resource allocation, content strategy, website optimization, and overall marketing effectiveness.
Calculated metrics can help you answer critical questions such as:
- Which marketing channels are driving the most valuable conversions?
- What content or pages are most engaging for your target audience?
- Where are you losing potential customers in your sales funnel, and how can you optimize that process?
- Are your marketing efforts delivering a positive return on investment?
By leveraging the insights gained from calculated metrics, you can make data-driven decisions that lead to improved business outcomes.
Best Practices for Using Calculated Metrics
To ensure you get the most value from your calculated metrics, consider the following best practices:
Align Metrics with Business Objectives: Carefully select the calculated metrics that align with your specific business goals and KPIs. Avoid creating metrics just for the sake of having more data.
Define Clear Metric Definitions: Provide clear and concise definitions for each calculated metric, explaining what it measures and how it can be interpreted.
Monitor Metric Trends: Regularly review the trends and changes in your calculated metrics over time. Look for patterns, anomalies, and opportunities for optimization.
Combine Metrics for Deeper Insights: Experiment with combining multiple calculated metrics to uncover more nuanced insights about your website's performance and user behavior.
Communicate Metric Findings: Share the insights gained from your calculated metrics with relevant stakeholders, such as marketing teams, product managers, and executives. Explain how the metrics support decision-making and drive business growth.
Continuously Refine and Iterate: Regularly review and update your calculated metrics as your business needs and goals evolve. Be open to experimenting with new metric formulas and adjusting existing ones as necessary.

By following these best practices, you can ensure that your calculated metrics are providing meaningful and actionable insights that drive informed decision-making and, ultimately, business success.
Conclusion
Google Analytics calculated metrics are powerful tools that can unlock deeper insights into your website's performance, user behavior, and marketing effectiveness. By going beyond the standard metrics and creating custom calculations tailored to your business needs, you can make more informed decisions that lead to better outcomes.
Whether you're optimizing your marketing campaigns, improving the user experience, or seeking to understand your customer journey in greater detail, calculated metrics can be a game-changer in your data analysis and decision-making processes.
So, start exploring the world of calculated metrics in Google Analytics, and unlock the full potential of your data to propel your business forward.