
How ssl seo improves your website security and rankings
Learn how SSL SEO not only secures your website but also drives higher Google rankings by boosting t...

Adding hreflang and x-default tags is vital for websites that cater to visitors from different languages or parts of the world. These tags act as friendly guides for search engines and help them pick the right page version based on a user's language or location. You dodge duplicate content headaches and offer visitors an experience that feels tailor-made for them.
The hreflang attribute is like a helpful signpost that tells search engines the language—and sometimes the region—of a webpage version, making sure users land on the page that suits them best. The x-default tag acts as the safety net, marking the fallback or default page displayed when there isn’t a perfect language or region match to be found.
If hreflang and x-default tags are missing, search engines can get tripped up and mistake your multilingual pages for duplicates which hurts your rankings. On top of that, users might land on pages in the wrong language or region. This creates a confusing experience that can send your bounce rates soaring.
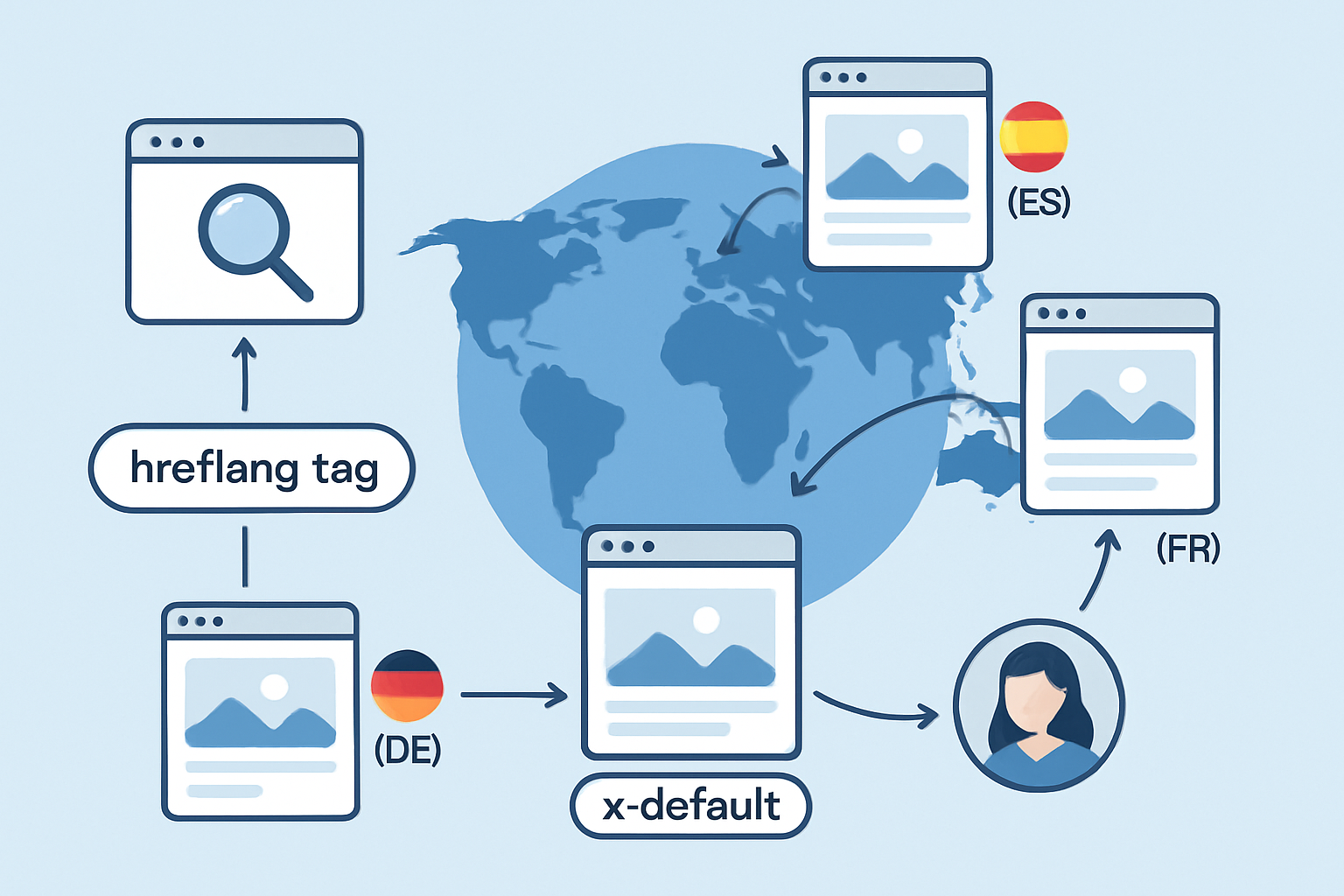
Visual diagram showing how hreflang and x-default direct users and search engines to the correct language version of a website
Double-check that you’ve got separate URLs for each language or regional flavor of your content. Each version should feature carefully tailored, localized material that really clicks with its intended audience. Don’t forget to nail down the correct ISO language and country codes—this little detail makes all the difference when it comes to proper identification.
Let's roll up our sleeves and walk through adding hreflang tags to your site, one step at a time. It might sound a bit technical, but with a little patience, you will have those tags working their magic in no time.
You can add hreflang tags in three main ways: using HTML link elements inside the
section, setting them via HTTP headers, or adding them to your XML sitemaps. Which route you take often depends on how your website is set up and what content management system you use.Kick things off by auditing your multilingual URLs to get a clear snapshot of all the language and regional versions currently live.
Take the time to nail down the correct ISO language and country codes for each version—it'll save headaches later.
Choose the smartest way to implement hreflang tags: go with HTML tags in headers if your site is small, sitemap annotations if you’re juggling bigger sites, or HTTP headers for tricky non-HTML files.
Craft your hreflang link tags with care, making sure each one has the right language-region code and points to the correct URL. No guessing games here.
Don’t overlook self-referencing hreflang tags—they’re your best friend to dodge errors.
Finally, put your setup through its paces using tools like Google Search Console or specialized hreflang validators to make sure everything is spot on.
For most websites, adding hreflang tags in the HTML
section is usually straightforward and works well, especially if your CMS lets you easily tweak page headers. For really large sites, XML sitemap annotations take the spotlight because they gather all hreflang URLs in one place for search engines. This setup helps you avoid pesky markup slip-ups. Also, do not forget HTTP headers since they are a lifesaver when dealing with non-HTML files like PDFs or images.The x-default tag is the safety net of your website, marking the default version of a page that users land on when there’s no exact language or regional match for their preferences. Typically, this points to a global homepage or a language-neutral landing page—think of it as the one-size-fits-all option. Making sure you’ve nailed down the right URL and consistently tagging it alongside other hreflang tags gives your users a reliable fallback.
If hreflang tags are not set up just right they can trip up your multilingual SEO instead of helping it. The usual suspects are using incorrect language codes and forgetting important reciprocal hreflang tags. Skipping the x-default tag, repeating hreflang entries, or mixing up languages and regions can also cause problems. These slip-ups tend to confuse search engines and lead to poor indexing and less accurate user targeting.
It is a good idea to kick things off by validating your hreflang code using some handy online tools. Next up, double-check that each page is playing nice with reciprocal links and that every language-region combo stays consistent and properly formatted—no loose ends here. Tools like Semrush or Ahrefs can really be your trusty sidekicks, helping you keep an eye on your hreflang setup as part of a wider SEO audit.
Testing and verifying hreflang and x-default tags is important to ensure your setup leads search engines and users down the right path. There are plenty of free and paid tools that can comb through your implementation and spot errors while giving you handy suggestions for improvement.
Your website grows and evolves it’s important to keep those hreflang and x-default tags fresh and accurate. A little regular upkeep goes a long way to ensure new language versions get the spotlight they deserve, while the outdated ones quietly fade away.

Learn how SSL SEO not only secures your website but also drives higher Google rankings by boosting t...

Discover how the Navboost algorithm transforms website navigation into a powerful ranking factor. Th...

Confused by 301 and 302 redirects? This guide explains their differences, SEO effects, and how to us...

Discover actionable SEO strategies to optimize Single Page Applications effectively. Use Semrush too...